Review Article
Teaching Knowledge Synthesis Methodologies in a Higher
Education Setting: A Scoping Review of Face-to-Face Instructional Programs
Zahra Premji
Research and Learning
Librarian
Libraries & Cultural
Resources
University of Calgary
Calgary, Alberta, Canada
Email: zahra.premji@ucalgary.ca
K. Alix Hayden
Senior Research Librarian
Libraries & Cultural
Resources
University of Calgary
Calgary, Alberta, Canada
Email: ahayden@ucalgary.ca
Shauna Rutherford
Information Literacy
Coordinator (Retired)
Libraries & Cultural
Resources
University of Calgary
Calgary, Alberta, Canada
Email: shauna.rutherford@ucalgary.ca
Received: 11 Jan. 2021 Accepted: 17 Mar. 2021
![]() 2021 Premji, Hayden, and Rutherford. This
is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons‐Attribution‐Noncommercial‐Share Alike License 4.0
International (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/),
which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium,
provided the original work is properly attributed, not used for commercial
purposes, and, if transformed, the resulting work is redistributed under the
same or similar license to this one.
2021 Premji, Hayden, and Rutherford. This
is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons‐Attribution‐Noncommercial‐Share Alike License 4.0
International (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/),
which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium,
provided the original work is properly attributed, not used for commercial
purposes, and, if transformed, the resulting work is redistributed under the
same or similar license to this one.
DOI: 10.18438/eblip29895
Abstract
Background - Knowledge
synthesis (KS) reviews are increasingly being conducted and published.
Librarians are frequently taking a role in training colleagues, faculty,
graduate students, and others on aspects of knowledge syntheses methods.
Objective - In order to
inform the design of a workshop series, the authors undertook a scoping review
to identify what and how knowledge synthesis methods are being taught in higher
education settings, and to identify particularly challenging concepts or
aspects of KS methods.
Methods - The following
databases were searched: MEDLINE, EMBASE & APA PsycInfo
(via Ovid); LISA (via ProQuest); ERIC, Education Research Complete, Business
Source Complete, Academic Search Complete, CINAHL, Library & Information
Science Source, and SocIndex (via EBSCO); and Web of
Science core collection. Comprehensive searches in each database were conducted
on May 31, 2019 and updated on September 13, 2020. Relevant conferences and
journals were hand searched, and forward and backward searching of the included
articles was also done. Study selection was conducted by two independent
reviews first by title/abstract and then using the full-text articles. Data
extraction was completed by one individual and verified independently by a
second individual. Discrepancies in study selection and data extraction were
resolved by a third individual.
Results - The authors
identified 2,597 unique records, of which 48 full-text articles were evaluated
for inclusion, leading to 17 included articles. 12 articles reported on credit
courses and 5 articles focused on stand-alone workshops or workshop series. The
courses/workshops were from a variety of disciplines, at institutions located
in North America, Europe, New Zealand, and Africa. They were most often taught
by faculty, followed by librarians, and sometimes involved teaching assistants.
Conclusions -
The instructional content and methods varied across the courses and workshops,
as did the level of detail reported in the articles. Hands-on activities and
active learning strategies were heavily encouraged by the authors. More
research on the effectiveness of specific teaching strategies is needed in
order to determine the optimal ways to teach KS methods.
Introduction
Knowledge
synthesis (KS), also known as evidence synthesis (ES), is defined as “the
contextualization and integration of research findings of individual research
studies within the larger body of knowledge on the topic” (Grimshaw, 2010, p. 2; Cochrane, 2020). Furthermore, KS uses methods
that are transparent and reproducible (Chandler & Hopewell, 2013).
There
are many types of knowledge synthesis reviews (Sutton et al., 2019), and one of the most well-known
is the systematic review (SR). A systematic review “seeks to collate evidence
that fits pre-specified eligibility criteria in order to answer a specific
research question” and attempts “to minimize bias by using explicit, systematic
methods documented in advance with a protocol” (Chandler et al., 2020, p. 1). SRs provide an up-to-date
synthesis of the state of knowledge on a topic, which can aid in decision-making
for practice or policy, identify and indicate gaps in knowledge or lack of
evidence, and reveal the limitations of existing studies on a topic (Lasserson et al., 2020). Whereas SRs have been prevalent
in the health sciences for some time, they are gaining popularity in a broader
range of disciplines.
While
systematic reviews are being increasingly published, many have incomplete
reporting or were conducted poorly (Bassani et al., 2019; Page et al., 2016; Pussegoda et
al., 2017). Experts recommend
that both researchers and journal editors should be better educated on SR
methodologies (Page & Moher, 2016; Page et al., 2016). They
specifically advocate for education focused on strategies to identify bias in a
SR, as well as strategies to minimize these biases, which will help to improve
the quality of published systematic reviews, and, subsequently, help to “reduce
this avoidable waste in research” (Page et al., 2016). Cochrane, an evidence synthesis
organization, recommends that first time review authors attend relevant
training and work with others who have experience conducting SRs (Lasserson et al., 2020).
Currently,
education on KS methods takes many forms such as higher education courses,
continuing education courses, workshops, webinars, and eLearning modules. Many
evidence synthesis organizations including Cochrane, Joanna Briggs Institute,
and the Campbell Collaboration offer fee-based workshops and courses that focus
on KS methods (Cochrane, n.d.; Campbell Collaboration, n.d.; Joanna
Briggs Institute, n.d.). SR instruction is also offered
as credit-bearing courses to undergraduate or graduate students in
post-secondary institutions (Himelhoch et al., 2015; Li et al., 2014). Some
professional development workshops on KS methods are available at conferences.
Additionally, academic libraries offer workshops on some steps of the
systematic review methodology (Campbell et al., 2016; Lenton & Fuller, 2019). All of these different
programs vary in terms of learner audience, breadth and depth of content
covered, and delivery methods, while having the shared goal of educating
researchers in the steps and processes necessary to conduct KS reviews.
Objectives
We
undertook the study as two of the authors were beginning to design of a series
of in-person workshops to teach systematic or scoping review methodology. We
wanted to learn which teaching methods work well and what challenges we might
encounter. We initially considered a systematic review, however, we realized
that we were conducting an exploratory study where the literature had not been
previously mapped in a structured way. Munn et al.
(2018) note that an
indication for conducting a scoping review is “to identify key characteristics
or factors related to a concept” (p. 2). Further, we wanted to include all
forms of evidence, including quantitative or qualitative studies, scholarship
of teaching reflections, opinion articles, and program descriptions. Given our
openness to all evidence types from all disciplines, we expected that the
retrieved literature could be quite heterogenous, which is one reason to choose
a scoping review (Peters et al., 2020). Scoping reviews “are more appropriate
to assess and understand the extent of the knowledge in an emerging field or to
identify, map, report, or discuss the characteristics or concepts in that
field” (Peters et al., 2020, p. 2121). Therefore, we decided that a scoping
review was the best approach to inform development of both the content and the
delivery of our workshop series.
The
objective of our scoping review was to identify the extent of the literature
and summarize articles that describe the teaching and learning of any knowledge
synthesis methodology in a post-secondary setting, with at least a partial
in-person (face-to-face) component, to determine:
1)
steps of the knowledge synthesis process taught
2)
teaching methods and learner activities used
3)
learner challenges encountered
A recent environmental scan focusing on online KS instructional courses
already exists (Parker et al., 2018). The
authors evaluated 20 online training resources against best practices for online
instruction using a rubric. To avoid duplication, we decided to exclude online
courses and focus solely on face-to-face educational options.
Methods
A protocol outlining the objectives, inclusion criteria, and methods for
this scoping review was developed in May 2019 to inform our study, and is
available from the first author. The protocol is based on the methodological
guidelines outlined by the Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) for the conduct of
scoping reviews (Peters et al., 2017).
Additionally, our study is reported according to the PRISMA-ScR
(Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis - Extension
for Scoping Reviews) guidelines (Tricco et al., 2018).
Study Eligibility
The population (P) in our scoping review is individuals at
post-secondary institutions, which includes students, staff, librarians, and
faculty. The concept (C) of interest is instructional interventions for
learning knowledge synthesis methodologies. The specific context (C) we are
interested in is non-commercial courses that had some in-person component.
Specifically, articles were eligible for inclusion if they describe a
course or workshop that:
●
taught knowledge synthesis methodology, which we
operationalized as the teaching of at least two steps of the knowledge
synthesis methodology (protocol development, question formulation, data
collection, study selection, data extraction, critical appraisal, narrative
synthesis, meta-analysis, or reporting)
●
was offered in a higher education setting (for
example, credit-bearing, professional development, optional workshop)
●
included at least some in-person components (blended
courses or entirely in-person course)
●
incorporated an evaluative, reflective, or assessment
component (this could take the form of assessments of student learning,
workshop/course evaluations, or instructor observations or reflection)
Additionally, articles were considered ineligible if they:
●
covered a course where teaching was entirely online or
via asynchronous methods
●
discussed commercially offered courses such as those
being offered by organizations involved in knowledge synthesis (e.g. Cochrane,
Joanna Briggs Institute, and others)
●
focused on evidence based medicine/practice, where
methodology of systematic reviews is not significantly covered
●
discussed only one step of the knowledge synthesis
methodology
● were published in languages other than English
Search Strategy and Information Sources
We utilized a three-step search strategy, as outlined by JBI (Peters et al., 2017). First,
we conducted an exploratory search in Google Scholar to discover relevant seed
studies that met the inclusion criteria for our review. The articles’ titles
and abstracts were analyzed and mined for keywords. As well, we analyzed the
seed article records in the MEDLINE (OVID) database to identify relevant
subject headings. From this analysis, a search was developed in MEDLINE (OVID),
and was piloted against the known seed articles to ensure relevant studies were
captured. This MEDLINE search was developed by a librarian (ZP) and
peer-reviewed by a second librarian (KAH). The search was then translated for
all databases identified in our search protocol. The searches incorporated
subject headings when available and free-text terms were combined using
appropriate Boolean operators. No language, date, or study design filters were
used. The complete search strategies for all databases are included in the
Appendix.
The choice of databases was purposefully exhaustive so that as many
different disciplines as possible would be represented in our scoping review.
The following OVID databases were searched:
·
MEDLINE(R) and Epub
Ahead of Print,In-Process
& Other Non-Indexed Citations and Daily (1946 – Sept 13, 2020),
·
EMBASE (1974 – Sept
13, 2020),
·
APA PsycInfo (1806 to Sept 13, 2020).
·
SocINDEX with Full-Text (1908 to Sept
13, 2020)
·
Education Research
Complete (1880 to Sept 13, 2020),
·
ERIC (1966 to Sept
13, 2020),
·
CINAHL Plus with
Full-Text (1937 to Sept 13, 2020),
·
Library and
Information Science Source (1901 to Sept 13, 2020),
·
Academic Search
Complete (1887 to Sept 13, 2020),
·
Business Source
Complete (1886 to Sept 13, 2020),
Additional databases searched included:
·
LISA: Library and
Information Science Abstracts (ProQuest, 1969 to Sept 13, 2020),
·
Web of Science Core
Collection. This core collection includes:
·
Science Citation
Index-Expanded (1900 to Sept 13, 2020),
·
Social Sciences
Citation Index (1900 to Sept 13, 2020),
·
Arts &
Humanities Citation Index (1975 to Sept 13, 2020),
·
Conference
Proceedings Citation Index - Science (1990 to Sept 13, 2020),
·
Conference
Proceedings Citation Index - Social Sciences & Humanities (1990 to Sept 13,
2020),
·
Emerging Sources
Citation Index (2005 to Sept 13, 2020).
Searches were conducted on May 31, 2019 and updated on September 13,
2020. Results were downloaded in RIS or text format, and deduplicated in
Covidence software ("Covidence," n.d.).
Our third and final step included the hand-searching of relevant
journals and conferences, as well as scanning the reference lists of included
articles and the associated cited-bys. We
hand-searched issues published within the last three years (2017-2019) of the
following journals: Journal of the Canadian Health Libraries Association,
Journal of the Medical Library Association, Evidence Based Library
and Information Practice, and Research Synthesis Methods. We also
hand-searched the programs from the following annual conferences: European
Association of Health Information and Libraries (2017-2019), Medical Library
Association (2017-2019), Canadian Health Libraries Association (2017-2019),
Association of European Research Librarian - LIBER (2017-2019), and Evidence
based Library and Information Practice (2019). Additionally, we conducted
forward and backward citation searching by scanning the reference lists and the
cited-bys (via Google Scholar) of all included
articles. Where further details were required, authors of the included studies were
contacted via email.
Study Selection
Study selection was conducted in two phases, first by title/abstract,
and then using the full-text. The process was completed in duplicate, using two
independent reviewers (ZP and SR). We first piloted a random set of 50 records
to ensure that the eligibility criteria were clear and consistently applied by
both screeners. A third independent reviewer resolved discrepancies (KAH). A
similar process was followed for the full-text screening, which was also done
independently in duplicate (ZP and SR), with a third reviewer resolving
discrepancies (KAH). Covidence software was used to facilitate the study
selection process.
Data Extraction
Data were extracted in Excel. The following categories were extracted
from each included article:
- author and
year
- title
- participants
(discipline and level)
- instructor
(librarian, faculty, or other)
- location of
course
- course
format/structure
- course-integrated
or stand-alone
- course
objectives
- steps of KS
methodology taught (specifically, defining the question, developing a
protocol, searching the literature, citation management, screening, data
extraction, narrative synthesis, meta-analysis, reporting, or critical
appraisal)
- assessment of
student learning/learner activities
- course evaluation/reflection
- outcomes of
course assessment
A data extraction template was created in Excel and was piloted by two
individuals independently, using 3 studies. Data extraction was then completed
by one individual (SR) and was verified independently by a second individual
(ZP). Verification was done by checking each data point extracted by the first
individual against the original source article. When discrepancies were found,
they were first discussed between the data extractor and data verifier. A third
individual reviewed any discrepancies in coding that were not easily resolved
through the initial consensus process (KAH).
Results
The data collection process identified 4,857 records for title/abstract
screening, of which 2,112 were duplicates. After applying inclusion criteria to
the 2,597 unique records, 48 articles were left for full-text screening. At the
end of the full-text screening process, 17 articles remained that met the
inclusion criteria for this scoping review. Inter-rater agreement for the
title/abstract screening was 98%, and for the full-text screening was 87%. The
inter-rater agreement was calculated automatically by Covidence and is the
proportionate agreement level between the two reviewers across the entire set
of records or articles. This means that the two reviewers voted the same way on
98% of the total records during title/abstract screening and 87% of the
articles during the full-text screening stages. The results of the study
selection process are reported in a modified PRISMA flow diagram (Moher et al., 2009) in
Figure 1 below.

Figure 1
PRISMA flow diagram.
Description of Included Articles
The population (discipline, learner level) and intervention
characteristics (course-integrated or stand-alone, instructors, location) of
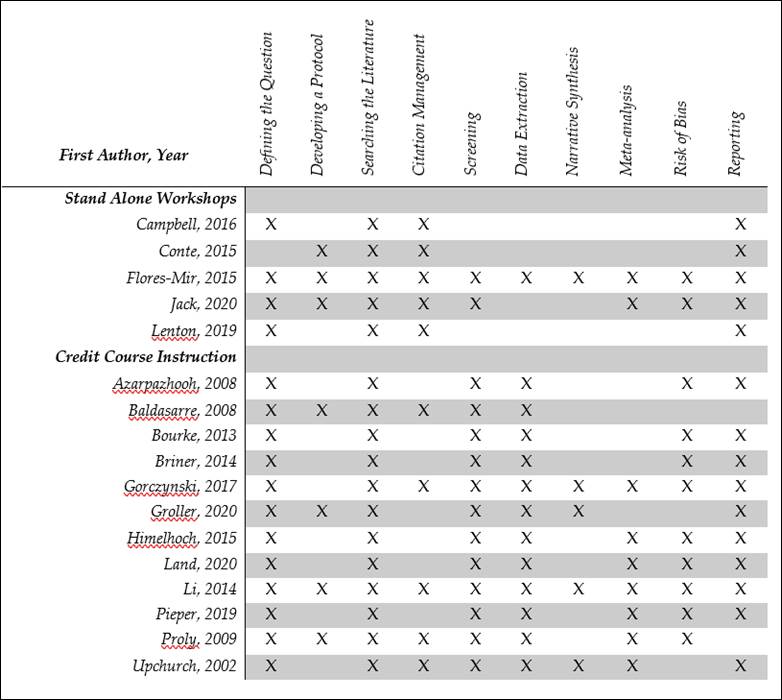
the 17 included articles in this review are shown in Table 1 below.
The majority of articles describe interventions from North America, with
six from the United States, and four from Canada. Three were located in the
United Kingdom, with an additional one each from Germany, Italy, New Zealand,
and Zimbabwe. Most instruction targeted graduate students as learners. The
majority (12) of the articles describe instruction where KS was the focus of an
entire credit course or where teaching KS was integrated into such a course,
whereas the other five articles describe stand-alone workshops. KS instruction
was taught to a broad range of disciplines. Many of the articles describe KS
instruction related to the health sciences (i.e., Dentistry, Nursing,
Biomedical Sciences, Exercise Science, Public Health and Speech Pathology)
which reflects the prevalence of KS in these disciplines. Faculty were involved
as instructors in all but three of articles, the remaining of which were taught
by librarians. In seven of the articles, teaching was shared to varying degrees
among faculty, librarians, teaching assistants and facilitators.
Inclusion criteria for our review dictated that all included workshops
or courses covered content related to at least two steps of the KS process, but
as Table 2 shows, most covered many more. The stand-alone workshops, which were
of shorter duration than the credit courses, included fewer steps of the KS
process. The three workshops taught exclusively by librarians (Campbell et al., 2016; Conte et al., 2015; Lenton & Fuller, 2019) taught
the fewest steps. This could be due to the fact that these workshops were
shortest in length, and also because the steps covered (problem definition,
searching, and citation management) are those that align most closely with
librarian expertise (Spencer & Eldredge, 2018). All 12
credit-bearing courses taught research question formulation, searching,
screening and data extraction. Two of the articles for course-based instruction
(Azarpazhooh et al., 2008; Groller
et al., 2020)
explicitly describe the teaching of five steps, whereas all other courses
covered six or more. The most commonly taught step was “Searching the
literature,” which all 17 articles describe. This was followed by “Defining the
Question” (16 articles), “Reporting” (15 articles) and “Screening” (14
articles). The least common step to be taught was “Narrative Synthesis” (five
articles).
Table 1
Population and Intervention Characteristics of Included Studies
|
Characteristic |
N |
||
|
Population |
|
|
|
|
Discipline |
|
|
|
|
|
Mixed |
3 |
|
|
|
Dentistry |
2 |
|
|
|
Nursing |
2 |
|
|
|
Biomedical
Sciences |
1 |
|
|
|
Business |
1 |
|
|
|
Educational
Psychology |
1 |
|
|
|
Engineering |
1 |
|
|
|
Exercise
Science |
1 |
|
|
|
Health
Economics Professional
Librarians |
1 1 |
|
|
|
Psychology |
1 |
|
|
|
Public
Health |
1 |
|
|
|
Speech
Pathology |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Learner
Level |
Graduate
Students Undergraduates Mixed Librarians |
9 4 3 1 |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
Intervention |
|
|
|
|
Workshop
Design |
|
|
|
|
Course
Integrated |
12 |
||
|
Stand-Alone |
5 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Instructors |
|
|
|
|
|
Faculty
Only |
7 |
|
|
|
Faculty
+ Librarian(s) |
4 |
|
|
|
Librarians
Only |
3 |
|
|
|
Faculty
+ TAs |
2 |
|
|
|
Faculty
+ Librarians + TAs |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Location |
|
|
|
|
|
United
States |
6 |
|
|
|
Canada |
4 |
|
|
|
United
Kingdom |
3 |
|
|
|
Germany Italy |
1 1 |
|
|
|
New
Zealand |
1 |
|
|
|
Zimbabwe |
1 |
Table 2
Steps of the Knowledge Synthesis Process that were
Taught in the Content of Each Course or Workshop
Our review captured a very diverse set of courses and workshops teaching
knowledge synthesis review methodology. Tables 3 and 4 display the summaries of
instruction interventions described in the included literature. The data are
presented in two tables, with course-based instruction and stand-alone
workshops displayed separately because of some clear differences between the
two types of offerings.
Table 3 presents a summary of the stand-alone workshops. All five
workshops included limited contact time with learners, ranging from three hours
in total (Campbell et al., 2016) to five
full days (Flores-Mir et al., 2015; Jack et al., 2020). The
course objectives for these workshops are stated in terms of preparing
attendees to participate in future reviews, which is appropriate given their
short duration. They aim to build capacity rather than to give students
extensive experience in conducting reviews. Librarians were the sole
instructors in three of the workshops (Campbell et al., 2016; Conte et al., 2015; Lenton & Fuller, 2019). The
workshops targeted a more diverse group of learners than the credit courses,
usually including a mix of levels (undergraduates, graduate students,
post-docs, researchers, librarians, professional staff). Also, without the
graded assignments available to instructors in a credit course, there were more
limited examples of student assessment. Two of the workshops (Campbell et al., 2016; Flores-Mir et al., 2015) do not
mention assessment of student learning at all. Two of the articles mention
conducting pretests and posttests (Conte et al., 2015; Jack et al., 2020), and two
articles describe assigning participants an assessment activity at the end of
the workshop (Jack et al., 2020; Lenton & Fuller, 2019). All of
the workshops offered some form of post-course evaluation survey.
The 12 credit courses are summarized in Table 4. Four of the courses
were offered to undergraduate students, while eight were at a graduate level.
Faculty members were the primary instructors for all the courses, and the sole
instructors for seven. Five articles (Briner & Walshe, 2014; Gorczynski et al., 2017; Groller et al.,
2020; Li et al., 2014; Proly & Murza, 2009)
explicitly mention librarian involvement either within the original course or
as a modification for later offerings based on feedback. The course objectives
generally focus on students developing an understanding of reviews and the
skills to conduct one. Some unique objectives include learning to teach others
about systematic reviews (Li et al., 2014) and
gaining project management skills and leadership experience (Proly & Murza, 2009). The
articles present a variety of graded assignments designed to assess student learning,
many of them tied to specific steps of the review process. Oral presentations
were assigned in five courses and students created a poster presentation for
one course (Bourke & Loveridge, 2013). Ten of
the courses required students to hand in either a written summary of findings
or a research manuscript based on their review. The most common form of course
assessment used was a post-course questionnaire or survey, mentioned in seven
articles. Groller et al. (2020) also
discusses an online survey specific to the information searching session
offered by the librarian. Other forms of course assessment include a focus
group (Azarpazhooh et al., 2008), student
self-assessments (Briner & Walshe, 2014), faculty
observations (Briner & Walshe, 2014), and an
analysis of student performance (Land & Booth, 2020).
One of the primary goals of this study was to
investigate instruction methods for teaching knowledge synthesis methodology.
Table 5 explores the variety of teaching and learning strategies implemented
for different steps of the knowledge synthesis process. We did not include
traditional lecturing as we were most interested in discovering active teaching
and learning strategies. The coding is not discreet - that is, multiple
learning strategies may be employed in teaching a single step. For example,
database searching may be coded as both hands-on and small group, as the participants
worked together to develop search strategies. The majority of articles only
briefly mention specific teaching and learning strategies. Li et al. (2014), for instance, states “we developed this course
with a philosophy of “learning by doing” (p. 255) but provides little detail on
the learning activities and teaching strategies used. Similarly, Jack et al. (2020) mentions that learners participated in interactive
exercises in groups; however, only one example is given. Pieper et al. (2019), who also
noted that they used a “learning by doing” philosophy, followed a unique
approach implementing a “guiding systematic review” which is a published
systematic review used as a “working example throughout the course” (p. 3). A
wide range of active learning and teaching strategies were employed across the
courses and workshops, with hands-on or small group activities being most
commonly mentioned. Hands-on activities were used most for teaching the steps
of question development, database searching, screening, data extraction, and
critical appraisal. These steps are mirrored in the small group activities, as
small group activities often included hands-on experiences.
Table 3
Summary of Workshop Characteristics
|
Author, Date, Country |
Discipline, level, workshop structure |
Instructors |
Course Objectives |
Assessment of Student
Learning |
Course Evaluation |
|
Campbell, 2016, Canada |
Mixed, students/faculty/ researchers, 3hr workshop |
Librarians |
Participants
will: identify systematic reviews, recognize the range of resources required
to execute a systematic review search, develop a well-formulated search
question and structure a search using the PICOS format, learn to apply
appropriate search limits, document a search in a standardized form,
understand the importance of peer-review of systematic review searches, and
recognize the level of expert searching needed for a systematic review |
|
Evaluation
questionnaire |
|
Conte, 2015, USA |
Mixed, Librarians, 2-day workshop |
Librarians |
Students
will gain knowledge of best practices in conducting systematic reviews and
create a personalized action plan to establish their libraries as centers of
expertise for systematic reviews |
Online pre and posttests, |
Online post-course survey, MLA evaluation form, Focus group |
|
Flores-Mir, 2015, Canada |
Dentistry, faculty/graduate
students/staff, 5 x 8hr sessions |
Faculty, Librarian (as guest lecturer) |
Students will broaden knowledge of evidence
based practice principles in Dentistry and gain hands-on experience in designing,
conducting, writing, and critiquing health care systematic
reviews. |
|
Post-workshop evaluation forms |
|
Jack, 2020, Zimbabwe |
Mixed, PhD/Post-doc/Librarians/ Program Managers, 5-day workshop |
Faculty |
To teach trainers from three African countries to conduct systematic
review workshops at their home institutions in order to broaden mental health
research capacity |
Online
pre and posttests, learner presentations at end of workshop |
post-workshop survey assessing learner satisfaction and perception of
confidence in conducting a SR |
|
Lenton, 2019, Canada |
Mixed, graduate students, 3 x 2.5hr sessions |
Librarian |
Students will learn to identify differences
between types of reviews, incorporate tools & resources for proper
reporting & management of the review, utilize strategies for creating a
searchable question with inclusion/exclusion criteria, identify relevant
databases, practice using a structured method for developing advanced search
strategies |
Student observation during activities,
ticket-out-the-door evaluation forms. Short post-course reflection
questionnaire |
Short post-course reflection questionnaire |
Table 4
Summary of Course Characteristics
|
Author, Date, Country |
Discipline, level, course structure |
Instructors |
Course Objectives |
Assessment of Student
Learning |
Course Evaluation |
|
Azarpazhooh, 2008, Canada |
Dentistry, Undergrad, 3 x 1hr lectures, 3 x 2-3hr
discussion sessions, 1 2-3hr presentation session |
Faculty,
Facilitators |
Students will
develop and apply skills in evidence based dental practice by finding
relevant literature, evaluating and
selecting the strongest evidence, summarizing findings, and communicating
results |
Students evaluated on
quality of participation in group discussions, group presentations and
on summary reports of findings |
Online pre and posttests,
online post-course survey, MLA evaluation form, focus group |
|
Baldasarre, 2008, Italy |
Electrical Engineering, Masters, 10 sessions |
Faculty, PhD Students |
Students will be introduced to empirical
research methods and trained to empirically evaluate software engineering
tools, techniques, methods and technologies |
Definition of research protocol assignment,
definition of inclusion/exclusion criteria assignment, data extraction
assignment |
Post-course
questionnaire |
|
Bourke, 2013, New Zealand |
Educational Psychology,
Masters, not specified |
Faculty |
Not provided in article |
Poster
presentations of initial finding of systematic reviews; students then submit
full systematic review incorporating faculty & peer feedback on posters. |
Student
self-assessments throughout course |
|
Briner, 2014, UK |
Business, Masters, 7 x 3hr sessions |
Faculty Librarian (as guest lecturer) |
Students will gain understanding of evidence
based practice and conduct a rapid systematic review |
5-minute presentation on the review
question. Research question and outline a few weeks before final
deadline. Rapid Evidence Assessment (max 4000 words), evaluated on a clear,
answerable review question, sound justification for conducting the review,
explicit search strategy, ways of judging the quality of the research, and
conclusions that accurately reflect the findings. |
Faculty observations of
student experience; student presentations had to answer question "what
problems or pleasant surprises have you encountered so far?” |
|
Gorczynski, 2017, UK |
Exercise Science, Masters, not specified |
Faculty |
Students will
learn to structure evidence based interventions and carry out valid and
reliable evaluations |
Students
identify an area of mental health and conduct a qualitative systematic review
that examines the impact of physical activity on their chosen mental health
topic. Solve weekly
case studies using new knowledge and lead discussions presenting their proposed
interventions and supporting rationale. |
Quantitative and
qualitative mid-year and year-end evaluations |
|
Groller, 2020, USA |
Nursing, Undergrad, approx. 120 hrs |
Faculty, Librarian |
Students will learn to design, conduct and
disseminate results of a collaborative scoping review |
Individual paper reviewing about seven
articles, determining suitability for answering research question, and then
summarizing implications for clinical practice, policy, education and further
research. Group oral presentation of research findings,
open to campus community. |
Online survey on library
session, with three open-ended questions. Online post-course evaluation
survey with 15 Likert-scale
& 4 open-ended questions |
|
Himelhoch, 2015, USA |
Psychology, Residents, 9 lectures |
Faculty |
Students will learn the
fundamentals of systematic reviews and meta-analysis, learn to select a good
research question, establish eligibility criteria, conduct a reproducible
search, assess study quality, organize data and conduct meta-analysis, and
present findings |
Eight assignments. 1) create
a PICO informed research question 2) Define and describe eligibility criteria
3) Conduct literature search and document results 4) Interrater reliability
assignment and PRISMA flow diagram 5) create risk-of-bias table and summary
table for included papers 6) Collect, organize, and document data to enable
calculation of weighted effect size 7) Present and interpret forest and
funnel plots 8) write scientifically formatted manuscript ready for peer
review. |
Anonymous course
evaluation - 38-questions on Likert scale + 3 open-ended questions |
|
Land, 2020, UK |
Biomedical Science, Undergrad, 3 x 2hr
classes, ongoing faculty consultation |
Faculty |
Students will develop the skills
to conduct an independently researched systematic review and meta-analysis
(SRMA) capstone project in their final year |
A systematic review and meta-analysis, done as
a proforma report |
Analysis of student
performance across program to measure effectiveness of the systematic review
exercise |
|
Li, 2014, USA |
Public Health, Masters &
PhD, 6hr/wk x 8 weeks |
Faculty,
Librarians, Teaching assistants |
Students will
learn the steps of performing systematic
reviews and meta-analyses and improve their ability to perform, critically
appraise, and teach others about systematic reviews |
Graded assignments include
three open-book quizzes, individually submitted review protocol, and
individually submitted final report on group's systematic review. Students
orally present reviews to class and respond to comment. |
Anonymous
evaluation before final paper. Post- course survey offered to students
who took course 2004-2012; second survey sent to past participants on
long-term effects of course. |
|
Pieper, 2019, Germany |
Health Economics, Undergrad, 1.5 hrs x 14 or 15
weeks |
Faculty |
Students will learn the
fundamentals of systematic review methodology and develop skills to
critically appraise other systematic reviews |
Students complete a 10-12 page systematic review
based on topics selected by instructor and reported according to PRISMA
guidelines |
Students complete a validated post-course
questionnaire to assess instructional quality |
|
Proly, 2009, USA |
Speech Language Pathology,
Masters & PhD, not specified |
Faculty,
Librarian (as guest lecturer) |
Students will:
develop understanding of intervention research design and clinical
implications of evidence based practice, develop analytical skills to assess
the quality of research evidence, gain project management
skills. Doctoral student will gain leadership experience. |
Major course assignment was
development of a coding form and code-book specific to each group’s topic,
research question and inclusion/exclusion criteria. Students also
had an assignment requiring hand calculation of effect sizes. All students
had to register their topic with the Education Coordinating Group of the
Campbell Collaboration. |
Not specified |
|
Upchurch, 2002, USA |
Nursing, Masters, not specified |
Faculty |
Course 1: Students will gain
skills to examine the literature, maintain a bibliographic database, practice
statistical analysis, select a problem area and type of data for a research
project. Course 2: Students will
complete the literature review or simple meta-analysis and prepare a written
report. |
Students do a class presentation of their
problem area, research question, background and significance. Students design
a coding sheet specific to their research question. Students write a
research manuscript emphasizing their methods, findings and
implications. |
Not specified |
Assessment Outcomes,
Student/Instructor Feedback, and Recommendations
Question Formulation and Refinement
Almost all of the included courses and workshops (16) teach question
formulation or topic refinement, which often also includes setting inclusion
criteria and limits. (see Table 2)
Determining and focusing the research question is an important first
step in a knowledge synthesis project. A broad question may be feasible for a
research team with many members working over an extended time period, but may
be overwhelming for a small group of students completing a course project. Some
articles report that students found this step challenging, either due to the
ambiguity and iterative nature of the question refinement process, or because
of the difficulty in finding a question that is manageable and appropriate for
a course assignment (Briner & Walshe, 2014; Upchurch et al., 2002). In one
article that describes two sequential research courses, graduate students
initially pick a topic of interest, although they do not complete a knowledge
synthesis project during the first course (Upchurch et al., 2002).
However, in the subsequent course the students take their previously-chosen
topic and refine it into a question appropriate for research synthesis. Upchurch et al. (2002) report
that developing the final research question and clarifying inclusion criteria
is an iterative process that students may find frustrating. The instructors
built in extra time at the beginning of the course for students to refine their
question. Even when students know they are picking a topic for the purpose of
conducting a small systematic review, the process of settling on an appropriate
review question can still be challenging. Briner and Walshe (2014)
emphasize this through a student’s quote, stating that they “really
underestimated the difficulty of asking the right question ahead of formulating
a search strategy” (p.426). They also mention that students were often
frustrated by the lack of consistency in the way that concepts were defined in
the literature, making it difficult to operationalize what seemed like a simple
idea or concept. This further adds to the difficulty in settling on an
appropriate research question.
Table
5
Teaching
and Learning Strategies for Knowledge Synthesis Steps
|
Knowledge Synthesis Step |
|
Teaching and Learning Strategies |
||||||||||
|
Hands-on Activities/ Experiential Learning |
Small Group Work/ Discussion |
Student Presentations |
Case Studies / Guiding Review |
Guided / Facilitated Exercises |
Individual Work |
Large Group Work/ Discussion |
Working in Pairs/ Pair Activities |
Reflection |
Peer Feedback/ Evaluation |
Role Playing |
Analyze Seminal Readings |
|
|
Protocol Development |
|
15 |
|
3 15 |
|
7 9 |
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Defining the Question |
1 6 10 11 13 |
1 2 4 7 10 |
1 4 6 |
3 15 |
6 |
6 |
4 |
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
Searching |
1 2 3 4
6 7 8 9 10
11 13 14
15 17 |
2 3 4 7
10 13 14
15 |
6 13 |
3 16 |
4 11 13 |
3 6 13 16 |
7 |
|
6 13 |
|
|
|
|
Screening Inclusion / Exclusion |
1 2 3 4
6 7 17 |
1 2 3 4 7
15 |
|
3 16 17 |
|
15 16 |
15 |
6 17 |
|
|
|
|
|
Citation/Reference Management |
1 4 7 |
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Data Extraction |
1 2 3 4
6 7 9 17 |
1 2 3 4
7 15 |
|
3 17 |
3 4 |
3 15 16 |
15 |
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
Critical Appraisal / Risk of Bias |
2 4 7 10
17 |
2 4 7 10 |
|
16 17 |
|
16 |
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Synthesis |
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Meta-Analysis |
1 7 10 17 |
1 7 10 |
|
17 |
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Manuscript Draft/ Completed Review |
10 |
2 7 10 |
2 5 6 7
10 15 |
|
|
1 7 15 16 |
2 |
|
|
1 5 |
|
|
|
Reporting / Data Management |
13 17 |
13 |
|
17 |
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Phase not specified |
|
8 |
|
12 |
16 |
8 |
8 12 |
|
|
2 |
8 |
12 |
|
|
1 Upchurch, 2002 |
5 Bourke, 2013 |
9 Flores-Mir, 2015 |
13 Lenton, 2019 |
17 Pieper, 2020 |
|
|
2 Azarpazhooh, 2008 |
6 Briner, 2014 |
10 Himelhoch, 2015 |
14 Jack, 2020 |
|
|
|
3 Baldassarre, 2008 |
7 Li, 2014 |
11 Campbell, 2016 |
15 Groller, 2020 |
|
|
|
4 Proly, 2009 |
8 Conte, 2015 |
12 Gorczynski, 2017 |
16 Land, 2020 |
|
One strategy to simplify the process of research question development is
for the course instructors to pick a list of topics that they know may be
feasible for a course assignment. In one course, this was done effectively by
using a set of topics or areas of focus that were important to stakeholders as
a starting point from which to develop a relevant question (Bourke & Loveridge, 2013). In Pieper et al. (2019) and Land and Booth (2020),
students were either given a specific topic or selected from a carefully
curated list of topics; topics were vetted by the instructor in order to ensure
a manageable volume of results from the search. However, Li et al. (2014) describe
another situation where, despite best intentions and a clear set of criteria,
some of the topics suggested each year “result in students’ searches that
identify tens of thousands of titles and abstracts requiring screening or many
more primary research articles meeting the students’ inclusion criteria” (p.
258). Therefore, further intervention and guidance is required from the
instructors on how to narrow a topic. However, selecting appropriate topics for
students is a challenging task. Pieper et al. (2019) discuss
some criteria they felt would be appropriate when identifying suitable topics,
such as a small number of search terms and synonyms, reasonable volume of
search results, and so on.
Several articles suggest highlighting the difficulty and importance of
rigorous question formulation (Briner & Walshe, 2014; Gorczynski et al., 2017; Upchurch et al.,
2002).
Furthermore, students learned the importance of the research question in
determining the body of evidence (Baldassarre et al., 2008) and of
choosing the right question (Briner & Walshe, 2014).
Protocol Development
Developing a protocol was either taught or
assigned as an assessment of student learning in seven of the courses or
workshops. In one class, determining inclusion/exclusion criteria, collecting
search terms, and defining the data extraction criteria were assigned as
homework , and in the following class students discussed their submissions (Baldassarre et al., 2008). Although not explicitly about protocol
development, students in one course requested
additional information and assistance with setting inclusion criteria which is
one of the components that needs to be defined in a protocol (Gorczynski et al., 2017). In Li et al. (2014),
creating the protocol was worth a significant portion of their final course
grade, and students suggested that this be a group assignment rather than an
individual assignment. Protocol development as a group reflects the real-life
experience of researchers when developing their review protocol as a team. In Proly and Murza (2009), the
goal of the 15-week course was to submit a review title and protocol to the
Campbell Collaboration.
Searching for Studies (Data Collection)
In all of the 17 included articles, searching for evidence was taught as
part of the course or workshop.
Searching for KS research must be comprehensive and exhaustive, and
attempts must be made to gather all relevant evidence. For students conducting
a KS project for the first time, this level of comprehensiveness in searching
is likely new. KS course assignments may not require the level of exhaustive
searching expected in a full KS review, however the level of comprehensiveness
required is still likely greater than what students may be doing for other
assignments. In faculty-led courses or workshops, librarians were sometimes
invited to teach the search process; this was mentioned in six articles (Briner & Walshe, 2014; Flores-Mir et al., 2015; Gorczynski et al.,
2017; Groller et al., 2020; Li et al., 2014; Proly & Murza, 2009).
Student feedback suggests that they recognized the importance,
difficulty, or time-consuming nature of searching for evidence (Baldassarre et al., 2008; Briner & Walshe, 2014; Groller et al.,
2020). They
suggested that more time be allocated for learning how to search, and that
additional guidance or handouts to aid with searching be included as part of
the content (Campbell et al., 2016; Gorczynski et al., 2017; Lenton & Fuller,
2019). Groller et al. (2020) report
that the librarian provided additional, unplanned sessions with each group in
order to meet the criteria set out in the pre-established search protocol.
These consultations with librarian search experts were found to be beneficial.
Despite the challenges, students felt that their experiences in the courses led
to improved abilities, skills, or confidence in gathering, searching, or
locating evidence (Azarpazhooh et al., 2008; Conte et al., 2015; Proly & Murza, 2009). The
course described by Groller et al. (2020) included
an evaluation of the library research session. Student feedback highlighted
learning about new databases, learning the different way that searches can be
executed, and noting that the library skills learned would have been useful
throughout their four years at university.
Study Selection and Data Extraction
Study selection and data extraction were taught in 13 courses/workshops
(see Table 2). All 12 articles that describe credit-bearing courses covered
both study selection and data extraction. Study selection is required to arrive
at a set of included studies from which data can be extracted and the evidence
synthesized. One of the stand-alone workshops (Jack et al., 2020)
discussed the step of study selection, but did not address data extraction.
Even though inclusion criteria are determined in the earlier stages of a
KS review, further refinement to the criteria can sometimes occur during the
study selection process. Additionally, reading and interpreting academic
literature are skills that are required within the study selection and data
extraction steps of a knowledge synthesis project. Reading, analyzing, and
interpreting academic research were reported as challenging by students (Briner & Walshe, 2014; Upchurch et al., 2002).
Students sometimes requested additional information or further assistance with
the process of extracting data (Gorczynski et al., 2017). Both
students and instructors suggested allocating more time for extracting data (Gorczynski et al., 2017; Li et al., 2014). Briner and Walshe (2014) state
that the process of developing and applying criteria for inclusion/exclusion
helps learners become active and critical consumers of information.
In Pieper et al. (2019),
students practiced data extraction by extracting data for one of the studies
included in a previously published systematic review; students then checked
their data extraction against the published systematic review, thus allowing
students to verify the accuracy of their work. In another course, students
participated in a pilot data extraction exercise in class to prepare them for
the data extraction process (Baldassarre et al., 2008).
Students had to independently extract data from one of two pre-selected papers,
and then compared their results with another student who worked on the same
paper. Eventually, students received the instructor’s data extraction for final
comparison. Feedback on the guided exercise was positive, but “some students
found it difficult to understand the meaning of the cells in the table”
(p.422). This exercise highlights the value of piloting the data extraction
process, but also demonstrates the challenges of the data extraction step.
Students also found it difficult to extract data from articles on unfamiliar
topics (Baldassarre et al., 2008). This
underscores the value of having some familiarity with the topic for data
extraction.
Synthesis and Critical Appraisal
5 articles cover narrative synthesis, 9 articles explicitly mention
meta-analysis, and 11 articles include the step of critical appraisal/risk of
bias (see Table 2).
Analysis or synthesis were either noted as challenging tasks (Upchurch et al., 2002) or
mentioned as particularly time-consuming, with a suggestion that additional
time be allocated to this step (Li et al., 2014).
However, students also felt that learning this step improved their ability to
analyze, critically evaluate, or apply information (Azarpazhooh et al., 2008; Groller et al., 2020; Proly & Murza,
2009). They
also became more critical of evidence (Bourke & Loveridge, 2013) or
skeptical of research findings (Briner & Walshe, 2014).
Students were surprised by the limited quantity, quality, and relevance of the
research they found. The synthesis and appraisal process thus allowed learners
to develop an awareness of the variations in quality and relevance of existing
research (Briner & Walshe, 2014). Students
improved their critical thinking skills and their ability to critique published
systematic reviews (Flores-Mir et al., 2015).
However, Land and Booth (2020) note
that students “tend to gloss over the detail of forest plots to focus on the
bottom-line result” or to focus on the basic interpretation of the funnel plots
“without attempting a deeper analysis of the data” (p.283). Suggestions and
guidance for addressing these challenges are also provided in their article.
Data Management, Documentation, and Reporting
Due to the volume of references or citations that need to be downloaded
and managed, and the explicit requirement to report every aspect of the
methods, data management, documentation and reporting are often taught as part
of both stand-alone workshops and credit courses. All 17 articles include
either data/citation management (10 articles), or documentation and reporting
(15 articles), and nearly half included both (see Table 2).
Conte et al. (2015) suggest
incorporating additional content on data management, reporting, and
documentation. Upchurch et al. (2002) suggest
that learners should keep a procedure manual to document the research process.
Introducing different reference management software is also recommended (Gorczynski et al., 2017). Campbell et al. (2016)
initially included a greater amount of time to cover reference management, but
time constraints resulted in less coverage in a later iteration of the
workshop. Instead, instructions on reference management were provided via
tutorials made available prior to the in-class workshop.
Instructional Design
and Teaching Strategies
In addition to discussing challenges, feedback, suggestions, or
recommendations related to course content, many articles discuss instructional
design or course structure. Azarpazhooh et al. (2008) mention
that frequent, shorter sessions were preferred over a longer 3-hour session,
however Lenton and Fuller (2019) state
that students in their workshops preferred longer sessions in order to more
fully cover the content. Allowing more time for learning activities, hands-on
practice, or group work is suggested in many articles (Campbell et al., 2016; Flores-Mir et al., 2015; Gorczynski et al.,
2017; Li et al., 2014).
There is no consensus on whether group or individual assignments are
preferred, however many articles stress the value of students working
collaboratively with peers or advisors throughout the review process. Li et al. (2014) mention
that assignments should be group rather than individual, whereas Conte et al. (2015) suggest
that the group project be changed to an individual assignment. Pieper et al. (2019) included
in-class activities completed in pairs or groups, however the course assignment
was done individually. Incorporating peer activities and regular feedback from
instructors is also mentioned in the literature. Upchurch et al. (2002) and Himelhoch et al. (2015) write
about the value of consulting with peers or faculty, while Baldassarre et al. (2008) mention
that group discussions with peers was motivation for students to complete their
assigned tasks. Land and Booth (2020)
encouraged students to share search strategies on a discussion board, which is
another form of peer learning. Pieper et al. (2019)
incorporated frequent contact with the instructor during search development,
and students were required to have their search approved by the instructor
before continuing on to the next step.
There are a few other note-worthy recommendations. Gorczynski et al. (2017) and Upchurch et al. (2002) both
suggest working with external experts such as methods or information experts.
Furthermore, both Groller et al. (2020) and Li et al. (2014) discuss
the value of integrating an information literacy expert into the course. Campbell et al. (2016) and Gorczynski et al. (2017) mention
providing or requiring readings in advance and providing more information in
general. A structured stepwise approach to the content (Himelhoch et al., 2015) and
consistency and repetition (Gorczynski et al., 2017) are
discussed. The provision of examples for in-class activities or course
assignments is also suggested (Baldassarre et al., 2008; Conte et al., 2015). Pieper et al. (2019) describe
their approach of using a “guiding systematic review” (p.3) which is an
existing published systematic review. The authors suggest using a systematic
review that is well-conducted and has high reporting quality. During class,
students complete various tasks related to specific steps of a systematic
review, and compare their results to those in the chosen “guiding systematic
review.” The major benefit for this approach is the ability for students to
reproduce some of the work and compare their work to the published results.
The use of active learning and hands-on practice is also mentioned both
in general (Conte et al., 2015; Flores-Mir et al., 2015; Jack et al., 2020; Lenton
& Fuller, 2019; Pieper et al., 2019) and in
regard to specific steps of the knowledge synthesis process. In terms of
learner baseline knowledge, it is recommended that instructors assume learners
have no working knowledge of the topic or only basic skills (Campbell et al., 2016; Gorczynski et al., 2017). A
further suggestion is to cover students’ muddiest points from the previous
session at the beginning of the next session so as to ensure that everyone is
on the same page (Lenton & Fuller, 2019).
Student engagement with the content is another theme in a number of
articles. Briner and Walshe (2014)
emphasize the importance of students choosing their own research questions for
this reason. Given the challenging nature of conducting a review, “it is more
likely that students will stay motivated if they have chosen a topic that
interests them” (Briner & Walshe, 2014, p. 425). Gorczynski et al. (2017) suggest
making “the experience fun and enjoyable by allowing students to lead seminars
and bring in their own reviews” (p. 13). The capstone project in the workshop
described by Conte et al. (2015),
included “a personalized action plan tailored to the unique needs, missions,
organizational goals, and resources of the librarians’ home institutions” (p.
71). Jack et al. (2020) required
participants to be involved in a systematic review in order to participate in
the workshop; this ensured meaningful engagement with the skills and concepts,
as participants had to immediately apply them to an existing project. In
addition to being a motivating factor, real-life projects also generate
complexities and issues to be resolved, and these can provide additional
learning that may not happen with a perfectly designed course assignment. This
can be both a challenge and a benefit, as excessively complex issues may
frustrate the learner in the moment, but in the right dose may lead to
opportunities for deeper learning.
Benefits of Participation
in a Knowledge Synthesis Course/Workshop
Despite the complexity and challenge of teaching knowledge synthesis
methodology, especially in a course setting, instructors and students alike
found many benefits from the experience. Students developed a greater
appreciation of the importance of evidence based clinical practice (Azarpazhooh et al., 2008) or
increased knowledge of evidence based practice (Flores-Mir et al., 2015). In one
course, for example, a student mentioned learning “the importance of balancing
research with stakeholder opinions” (Bourke & Loveridge, 2013, p. 19).
Students developed increased skills, confidence, or motivation (Campbell et al., 2016; Flores-Mir et al., 2015; Himelhoch et al., 2015;
Jack et al., 2020) or even
feelings of empowerment (Briner & Walshe, 2014).
Developing communication skills (Azarpazhooh et al., 2008), and “a
new ability to incorporate the learned material into their classroom lectures
or clinical bedside teaching” (Flores-Mir et al., 2015, p. 4) are also
mentioned. Interestingly, students also learned the importance of teamwork in
the research process (Groller et al., 2020).
Another point commonly arising from the literature is that learners not
only gained the skills to conduct knowledge synthesis reviews, they also became
better and more critical consumers of research. Bourke and Loveridge (2013) provide
a series of students quotes emphasizing this concept, including “Because of
this course I now not only look at the evidence supporting the research I read,
but I also think about how that evidence was obtained” and “When I read about
research in the media I wonder about the study’s methodological quality, how
this might have influenced the results, and how the study compares to others”
(p. 19). Li et al. (2014) surveyed
past students, discovering that one of the long-term impacts of the course was
an increased ability to appraise reports of systematic reviews and other
primary studies (p. 263). Therefore, even those students who may not complete
another knowledge synthesis review benefit from taking a KS course in terms of
their development as student researchers.
Discussion
The courses and workshops discussed in our scoping review are diverse in
structure, learner population, academic discipline, and location, making them a
challenge to synthesize. Furthermore, some articles provide rich information
and detailed descriptions, whereas others include very few specifics about the
instructional content or teaching and learning strategies. Therefore, it is not
surprising that the recommendations emerging from the included articles are
also diverse, regarding both content and instructional design choices. There
are, however, some common themes that emerge.
Several articles describe similar features regarding course or workshop
design. KS methodology is complex, requiring an understanding of both the
conceptual underpinnings of the process as well as the practical
implementation. Consequently, the articles we found frequently mention
providing both prescriptive information on how specific steps of a knowledge
synthesis review are conducted along with opportunities for hands-on learning
and practice. Recommendations to allocate additional time for specific steps of
a review also arise several times in the literature. Additionally, group-work
is mentioned frequently. These suggestions touch on aspects that are common in
the process of conducting a systematic review, meta-analysis, or other KS
review; reviews should be conducted in teams, require a significant amount of
time, and have many intricate steps that need to be followed (Higgins et al., 2020).
Most courses and workshops included in our review incorporated active
learning, which led to student engagement. Active learning, as defined by Bonwell and Eison (1991) in their
seminal work, includes instructional activities which “involve students in
doing things and thinking about what they are doing” (p. 2). Student engagement
is a “process and a product that is experienced on a continuum and results from
the synergistic interaction between motivation and active learning” (Barkley & Major, 2020, p. 8). Through
the incorporation of various active learning activities, such as collaborative
group activities, case studies, hands-on practical exercises, individual and
group projects, and presentations, students experience “real world” knowledge
synthesis research. Students thereby develop a better understanding of the
steps associated with the KS methodology, and, as with the students in the
course described by Jack et al. (2020), they
may be motivated and confident to conduct their own KS project.
Some longer-term benefits or outcomes of the instruction are also
mentioned, including: interest in carrying out another systematic review (Baldassarre et al., 2008);
interest in future presentation, publication, or professional development (Proly & Murza, 2009); and
subsequent publications, conference abstracts, or dissertation topics that
resulted from the course assignments (Briner & Walshe, 2014; Himelhoch et al., 2015; Jack et al., 2020;
Li et al., 2014). The Land and Booth (2020) course
was scheduled in the penultimate year of the program in order to provide
students with the skills needed to conduct a systematic review/meta-analysis
capstone project in the final year. Case studies and student reflections have
shown that students perceive their participation in systematic reviews as
leading to their growth as student learners and researchers, and helps form
their identities as academics (Look et al., 2020; Pickering et al., 2015).
Implications for Practice and Future Research
When designing a course or
workshop on knowledge synthesis methods, many factors affect the choice of
course structure, teaching and learning strategies, activities and assignments.
In all cases, careful consideration of the baseline knowledge and skills of
learners is necessary. For example, undergraduate students may find it
challenging to read and understand the literature, so it may be necessary to
schedule more time for extracting or analyzing data when teaching these
learners than for a course for graduate students, post-docs or professionals.
If there is not time in the course or workshop to teach the necessary
foundational knowledge or skills (such as academic reading or basics of
research study design, etc.), then instructors should provide a set of
pre-course readings or tutorials and communicate explicit expectations to
ensure students are able to adequately prepare prior to attending. Pre-reading
and pre-work may help to avoid spending unplanned course time addressing
students’ lack of baseline knowledge. It may also prevent students who do have
the requisite baseline knowledge from being disengaged while the instructor
teaches basic concepts.
Overwhelmingly, the articles
in our scoping review advocate active learning and hands-on practice. Skills
such as searching, objectively applying inclusion/exclusion criteria, data
extraction, assessing risk of bias, and others need to be practiced in order
for learners to fully understand the messiness and complexity involved. The
specific teaching approaches used in the included articles varied, which is
similar to the approaches used to teach research methods in the social
sciences. Variability in teaching methods was highlighted in a review stating
that “authors advocate a range of approaches: exercises, problem‐based
learning, experiential learning, collaborative and group work, computer‐based
learning, tutorials, workshops, simulations and projects” (Wagner et al., 2011, p. 80). Sufficient time should be allocated to allow students to actively
participate and experience these knowledge synthesis steps. However, students
also need to be taught the conceptual underpinnings of the various KS steps,
and of the implications of the specific choices that they make, so that they
understand the importance of resolving issues based on methodological
principles.
The value of discussion,
consultation, and regular feedback is also emphasized in the included
literature. These elements should be built into the course to ensure students
have a way to assess their own progress and to ask for help as they work on
their reviews or assignments. While most stand-alone workshops or workshop
series are short and may not allow time for this, explicitly stating that
participants may reach out to workshop instructors in the future may serve a
similar purpose. Similar to feedback on a student’s assignment, these types of
one-on-one consultations with a librarian search expert providing personalized
and tailored guidance on a task associated with a student’s systematic review
project should be encouraged.
Given the increased focus on
reproducibility in the scientific literature in general, and in knowledge
synthesis in particular, instructors should ensure that students or
participants explicitly learn the difference between expectations for a course
assignment versus those for a publishable KS review. This ensures that
concessions made for course assignment feasibility are not replicated when
students later work on a KS review for submission to a journal. One way to help
students appreciate the full extent of work required for a publishable review
is to expose them to relevant methodological conduct guidelines from evidence
synthesis organizations in their disciplinary areas (Higgins et al., 2020;
Peters et al., 2017) which will demonstrate the expectations with regard to comprehensiveness,
rigor, and adherence to a strict methodological approach that are required to
produce a high-quality knowledge synthesis review. Furthermore, if a complete
review protocol or review manuscript is an assignment in the course,
instructors could require students to submit a completed PRISMA (Moher et al., 2009; Moher et al., 2015; Tricco et al.,
2018), or other reporting checklist along with their submission to reinforce
reporting expectations. Such an assignment would encourage best practices, and
may contribute to a reduction in the poor reporting currently being observed in
published reviews (Bassani et al., 2019; Page et al., 2016).
Additionally, there is a
potential for greater librarian involvement in the teaching of knowledge
synthesis. Librarians have reported involvement in all steps of the systematic
review process, as well as other roles such as peer review, evaluation, and
teaching (Spencer & Eldredge,
2018). The positive impact of librarian involvement on the quality of the
review has also been reported (Meert et al., 2016; Rethlefsen et al., 2015). Furthermore, librarians trained in KS methods have both methodological
expertise and information science expertise and are therefore ideal
collaborators, co-instructors, or guest lecturers for faculty-led KS courses (Wissinger, 2018). Li et al. (2014) refer to “the experience and engagement” of informationists as being “a
key contributor to the success of the course” and further state that librarians
“contribute by lecturing, advising, modeling the benefit of collaborating with
experts, and signing off on search strategies” (p.261).
As search experts,
librarians should be teaching the searching section of a KS course (McGowan & Sampson,
2005). Librarian involvement is mentioned in 5 of the 11 credit course
articles, though it is possible that librarians were involved in the other
courses but not explicitly mentioned. Of these five articles, four were about
KS courses in medical and allied health disciplines including public health,
speech language pathology, nursing, and exercise science. This comes as no
surprise as librarians in health-related disciplines have an established role
in KS, and guidance documents recommend working with a librarian to develop and
implement the search for evidence (Lefebvre et al., 2020). In other disciplines, however, this may still be an emerging role and
is therefore an area of potential growth for librarians working in these
fields.
Further research focused on
teaching knowledge synthesis methods is required. Despite the growth of
knowledge synthesis reviews published in the academic literature, there is a
very limited number of articles published on how the methodology is taught in
higher education settings. We found only 17 articles that met our inclusion
criteria. More program descriptions and evaluation studies are needed that show
what content is covered, how the content is taught, and which instructional
strategies are successful for teaching the various steps of knowledge syntheses
methods.
Strengths and
Limitations
Strengths of our study include the following. We utilized a robust
methodology used to identify and synthesize the literature on this topic. We
searched 12 databases, including both subject-specific and multidisciplinary
ones. We also hand searched related journals’ tables of contents and conference
proceedings. Prior to screening, we piloted our inclusion/exclusion criteria on
50 random titles/abstracts. Further, we contacted authors to verify information
and course descriptions when necessary.
However, despite our rigorous methodology and exhaustive search
strategy, it is possible that we missed potentially relevant articles. One
limitation of our review is that we only included articles that were published
in English. Additionally, the selection of conferences to hand-search were
limited to known, major health or evidence based practice related librarian
conferences in North America and Europe. Our choices were based on our existing
knowledge of the types of conferences more likely to contain presentations
about systematic review workshops. However, knowledge synthesis is not limited
to a specific discipline or geographic area, and it was not feasible to search
conferences across all disciplines and across all regions, so this is a further
limitation to our study.
Another limitation is that we used adjacency for searching the two
concepts near each other, which affects the sensitivity of the search strategy.
However, a balanced approach was required, in order to prevent retrieving every
knowledge synthesis review about teaching and learning, and to ensure the
process/scope would be feasible. To overcome this, as noted above, we searched
a wide variety of databases from different disciplines and supplemented the
database searches with supplementary searching.
Not all of the included articles provide a high level of detail about
the learning objectives/outcomes, specific in-class activities and assessments,
teaching strategies, or outcomes with the published article. Therefore, it is
possible that some courses included more than is reported in our scoping
review.
Conclusion
Our scoping review aimed to summarize the extent of the literature on
courses and workshops that teach KS methods. The 17 included articles helped
further our understanding of what content is taught, which instructional
methods are commonly used, and what outcomes are achieved through teaching KS.
Common elements that arose from the literature include a focus on active
learning and group work and an increase in participants’ skills and interest in
conducting systematic reviews. Our review results were limited because we only
included articles that contain an evaluative or reflective component rather
than ones that simply describe the programs. However, the assessment component
is what truly adds value to this review as it allowed us to determine what
parts of the process students find challenging and what the learners actually
gain through instruction. While identifying what is currently known about the
teaching of KS in higher education environments, as well as highlighting the
lack of articles that provide specific information on teaching and learning
strategies used, our review may inform the development and improvement of
courses or workshop teaching knowledge synthesis methodology.
Author Contributions
Zahra Premji: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation,
Methodology, Formal analysis, Project administration, Supervision, Visualization,
Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing K. Alix Hayden: Conceptualization,
Funding acquisition, Investigation, Formal analysis, Visualization, Writing -
original draft, Writing - review & editing Shauna Rutherford: Investigation,
Formal analysis, Visualization, Writing - original draft, Writing - review
& editing
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge funding from a Development and
Innovation, Teaching and Learning Grant funded by the Provost’s Office,
University of Calgary. We would also like to thank Dr Justine Wheeler,
Assessment, Social Work and Sociology Librarian, Libraries & Cultural
Resources, University of Calgary and Robin Parker, Evidence Synthesis
Librarian, W.K. Kellogg Health Sciences Library, Dalhousie University for
reviewing and providing suggestions and feedback on our manuscript.
Azarpazhooh, A., Mayhall, J. T.,
& Leake, J. L. (2008). Introducing dental students to evidence-based
decisions in dental care. Journal of
Dental Education, 72(1), 87-109. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.0022-0337.2008.72.1.tb04457.x
Baldassarre, M. T., Boffoli, N., Caivano, D., &
Visaggio, G. (2008). A hands-on approach for teaching systematic review. In Product-Focused Software Process
Improvement, Proceedings (Vol. 5089, pp. 415-426). Springer-Verlag Berlin.
Barkley, E. F., & Major, C. H. (2020). Student engagement techniques: A handbook
for college faculty. John Wiley & Sons.
Bassani, R., Pereira, G. K. R., Page, M. J., Tricco,
A. C., Moher, D., & Sarkis-Onofre, R. (2019). Systematic reviews in
dentistry: Current status, epidemiological and reporting characteristics. Journal of Dentistry, 82, 71-84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdent.2019.01.014
Bonwell, C. C., & Eison, J. A. (1991). Active learning: Creating excitement in the
classroom. 1991 ASHE-ERIC Higher Education Reports: ERIC.
Bourke, R., & Loveridge, J. (2013). A
scientist-practitioner model for inclusive education: Supporting graduate students
to conduct systematic reviews for evidence-based practice. New Zealand Journal of Teachers' Work, 10(1), 4-23.
Briner, R. B., & Walshe, N. D. (2014). From
passively received wisdom to actively constructed knowledge: Teaching
systematic review skills as a foundation of evidence-based management. Academy of Management Learning &
Education, 13(3), 415-432. https://doi.org/10.5465/amle.2013.0222
Campbell Collaboration (n.d.). Training. https://campbellcollaboration.org/research-resources/training-courses.html
Campbell, S. M., Kung, J. Y. C., & Dennett, L.
(2016). A curriculum for an introductory systematic review searching workshop
for researchers. The Journal of the
Canadian Health Libraries Association = Journal de l'Association des
Bibliothèques de la Santé du Canada, 37(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.5596/c16-003
Chandler, J., Cumpston, M., Thomas, J., Higgins, J.
P. T., Deeks, J. J., & Clarke, M. J. (2020). Chapter 1: Introduction. In J.
P. T. Higgins, J. Thomas, J. Chandler, M. Cumpston, T. Li, M. J. Page, & V.
A. Welch (Eds.), Cochrane handbook for
systematic reviews of interventions (Vol. 6.1). https://training.cochrane.org/handbook
Chandler, J., & Hopewell, S. (2013). Cochrane
methods-twenty years experience in developing systematic review methods. Systematic Reviews, 2(1), 76. https://doi.org/10.1186/2046-4053-2-76
Cochrane. (n.d.). About Cochrane training. https://training.cochrane.org/about-cochrane-training
Cochrane. (2020). Evidence synthesis - What is it
and why do we need it? https://www.cochrane.org/news/evidence-synthesis-what-it-and-why-do-we-need-it
Conte, M. L., MacEachern, M. P., Mani, N. S.,
Townsend, W. A., Smith, J. E., Masters, C., & Kelley, C. (2015). Flipping
the classroom to teach systematic reviews: The development of a continuing
education course for librarians. Journal
of the Medical Library Association, 103(2), 69-73. https://dx.doi.org/10.3163%2F1536-5050.103.2.002
Covidence. (n.d.). Melbourne, Australia. https://www.covidence.org/
Flores-Mir, C., Pacheco-Pereira, C., De Luca Canto,
G., Elyasi, M., & Saltaji, H. (2015). Oral health research methods summer
institute: A systematic review methodology workshop. Journal of the Canadian Dental Association, 81, f17. https://jcda.ca/article/f17
Gorczynski, P., Burnell, K., Dewey, A., &
Costello, J. T. (2017). Teaching evidence-based synthesis: An examination of
the development and delivery of two innovative methodologies used at the
University of Portsmouth. Journal of
Evidence-Based Medicine, 10(1), 11-15. https://doi.org/10.1111/jebm.12241
Grimshaw, J. (2010). A knowledge synthesis chapter. https://cihr-irsc.gc.ca/e/documents/knowledge_synthesis_chapter_e.pdf
Groller, K. D., Adamshick, P., & Petre, K.
(2020). Embracing evidence-based nursing and informational literacy through an
innovative undergraduate collaborative project. International Journal of Nursing Education Scholarship, 18(1), 1-9.
https://doi.org/10.1515/ijnes-2019-0138
Higgins, J. P., Thomas, J., Chandler, J., Cumpston,
M., Li, T., Page, M. J., & Welch, V. A. (2020). Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions [6.1]. https://training.cochrane.org/handbook
Himelhoch, S., Edwards, S., Ehrenreich, M., &
Luber, M. P. (2015). Teaching lifelong research skills in residency:
Implementation and outcome of a systematic review and meta-analysis course. Journal of Graduate Medical Education, 7(3),
445-450. https://doi.org/10.4300/JGME-D-14-00505.1
Jack, H. E., Merritt, C., Medhin, G., Musesengwa,
R., Mafuta, C., Gibson, L. J., Hanlon, C., Sorsdahl, K., Chibanda, D., & Abas,
M. (2020). Developing sustainable capacity-building in mental health research:
Implementation outcomes of training of trainers in systematic reviewing. Global Health Action, 13(1), 1715325. https://doi.org/10.1080/16549716.2020.1715325
Joanna Briggs Institute. (n.d.). Education: Short
courses. https://joannabriggs.org/education
Land, S. C., & Booth, D. (2020). Systematic
review and meta-analysis as a structured platform for teaching principles of
experimentation. Advances in Physiology
Education, 44(3), 276-285. https://doi.org/10.1152/advan.00131.2019
Lasserson, T.
J., Thomas, J., & Higgins, J. P. (2020). Chapter 1: Starting a review. In
J. P. T. Higgins, J. Thomas, J. Chandler, M. Cumpston, T. Li, M. J. Page, &
V. A. Welch (Eds.), Cochrane handbook for
systematic reviews of interventions (pp. 1-12). http://www.training.cochrane.org/handbook
Lefebvre, C., Glanville, J., Briscoe, S.,
Littlewood, A., Marshall, C., Metzendorf, M. I., . . . Thomas, J. (2020).
Chapter 4: Searching for and selecting studies. In J. P. T. Higgins, J. Thomas,
J. Chandler, M. Cumpston, T. Li, M. J. Page, & V. A. Welch (Eds.), Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of
interventions (pp. 67-107). https://training.cochrane.org/handbook
Lenton, E., & Fuller, K. (2019). Explaining the
method behind our madness: 3-part series on comprehensive searches for
knowledge syntheses. Journal of the
Canadian Health Libraries Association / Journal de l'Association des
bibliothèques de la santé du Canada, 40(1), 18-22. https://doi.org/10.29173/jchla29391
Li, T., Saldanha, I. J., Vedula, S. S., Yu, T.,
Rosman, L., Twose, C., Goodman, S. N., & Dickersin, K. (2014). Learning by
doing-teaching systematic review methods in 8 weeks. Research Synthesis Methods, 5(3), 254-263. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrsm.1111
Look, R., Shoemaker, H., Hoepner Jerry, K., &
Blake Margaret, L. (2020). Reciprocal benefits of engaging undergraduate
researchers in conducting a systematic literature review. Perspectives of the ASHA Special Interest Groups, 5(3), 699-709. https://doi.org/10.1044/2019_PERSP-19-00072
McGowan, J., & Sampson, M. (2005). Systematic
reviews need systematic searchers. Journal
of the Medical Library Association, 93(1), 74-80.
Meert, D., Torabi, N., & Costella, J. (2016).
Impact of librarians on reporting of the literature searching component of
pediatric systematic reviews. Journal of
the Medical Library Association, 104(4), 267. https://doi.org/10.3163/1536-5050.104.4.004
Moher, D., Liberati, A., Tetzlaff, J., Altman, D.
G., & The PRISMA Group. (2009). Preferred reporting items for systematic
reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Medicine, 6(7), e1000097. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097
Moher, D., Shamseer, L., Clarke, M., Ghersi, D.,
Liberati, A., Petticrew, M., Shekelle, P. Stewart, L. A. (2015). Preferred
reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P)
2015 statement. Systematic Reviews, 4(1),
1. https://doi.org/10.1186/2046-4053-4-1
Munn, Z., Peters, M. D., Stern, C., Tufanaru, C.,
McArthur, A., & Aromataris, E. (2018). Systematic review or scoping review?
Guidance for authors when choosing between a systematic or scoping review
approach. BMC Medical Research
Methodology, 18(1), 143. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-018-0611-x
Page, M. J., & Moher, D. (2016). Mass production
of systematic reviews and meta‐analyses: An exercise in mega‐silliness? The Milbank Quarterly, 94(3), 515. https://doi.org/10.1111/1468-0009.12211
Page, M. J., Shamseer, L., Altman, D. G., Tetzlaff,
J., Sampson, M., Tricco, A. C., Catalá-López, F., Li, L., Reid, E. K.,
Sarkis-Onofre, R., & Moher, D. (2016). Epidemiology and reporting
characteristics of systematic reviews of biomedical research: A cross-sectional
study. PLoS Medicine, 13(5),
e1002028. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1002028
Parker, R. M., Boulos, L. M., Visintini, S.,
Ritchie, K., & Hayden, J. (2018). Environmental scan and evaluation of best
practices for online systematic review resources. Journal of the Medical Library Association, 106(2), 208. https://doi.org/10.5195/jmla.2018.241
Peters, M. D., Godfrey, C., McInerney, P., Baldini
Soares, C., Khalil, H., & Parker, D. (2017). Chapter 11: Scoping reviews. Joanna Briggs Institute Reviewer's Manual.
Peters, M. D., Marnie, C., Tricco, A. C., Pollock,
D., Munn, Z., Alexander, L., McInerney, P., Godfrey, C. M., & Khalil, H.
(2020). Updated methodological guidance for the conduct of scoping reviews. JBI
Evidence Synthesis, 18(10), 2119-2126. https://doi.org/10.11124/JBIES-20-00167
Pickering, C., Grignon, J., Steven, R., Guitart, D.,
& Byrne, J. (2015). Publishing not perishing: How research students
transition from novice to knowledgeable using systematic quantitative
literature reviews. Studies in Higher
Education, 40(10), 1756-1769. https://doi.org/10.1080/03075079.2014.914907
Pieper, D., Muller, D., & Stock, S. (2019).
Challenges in teaching systematic reviews to non-clinicians. Zeitschrift fur Evidenz, Fortbildung und Qualitat im Gesundheitswesen,
147-148(101477604), 1-6. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.zefq.2019.10.004
Proly, J. L., & Murza, K. A. (2009). Building
speech-language pathologist capacity for evidence-based practice: A unique
graduate course approach. Evidence-Based
Communication Assessment and Intervention, 3(4), 220-231. https://doi.org/10.1080/17489530903432383
Pussegoda, K., Turner, L., Garritty, C., Mayhew, A.,
Skidmore, B., Stevens, A., Boutron, I., Sarkis-Onofre, R., Bjerre, L. M.,
Hróbjartsson, A., Altman, D. G., & Moher, D. (2017). Systematic review
adherence to methodological or reporting quality. Systematic Reviews, 6(1), 1-14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-017-0527-2
Rethlefsen, M. L., Farrell, A. M., Trzasko, L. C.
O., & Brigham, T. J. (2015). Librarian co-authors correlated with higher
quality reported search strategies in general internal medicine systematic
reviews. Journal of Clinical
Epidemiology, 68(6), 617-626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2014.11.025
Spencer, A. J., & Eldredge, J. D. (2018). Roles
for librarians in systematic reviews: A scoping review. Journal of the Medical Library Association, 106(1), 46. https://doi.org/10.5195/jmla.2018.82
Sutton, A., Clowes, M., Preston, L., & Booth, A.
(2019). Meeting the review family: Exploring review types and associated
information retrieval requirements. Health
Information & Libraries Journal, 36(3), 202-222. https://doi.org/10.1111/hir.12276
Tricco, A. C., Lillie, E., Zarin,
W., O’Brien, K. K., Colquhoun, H., Levac, D., Moher, D., Peters, M. D. J.,
Horsley, T., Weeks, L., Hempel, S., Akl, E. A., Chang, C., McGowan, J.,
Stewart, L., Hartling, L., Aldcroft, A., Wilson, M. G., Garritty, C., … Straus,
S. E.
(2018). PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR):
Checklist and explanation. Annals of
Internal Medicine, 169(7), 467-473. https://doi.org/10.7326/M18-0850
Upchurch, S., Brosnan, C. A., & Grimes, D. E.
(2002). Teaching research synthesis to advanced practice nurses. The Journal of Nursing Education, 41(5),
222-226. https://doi.org/10.3928/0148-4834-20020501-08
Wagner, C., Garner, M., & Kawulich, B. (2011).
The state of the art of teaching research methods in the social sciences:
Towards a pedagogical culture. Studies in
Higher Education, 36(1), 75-88. https://doi.org/10.1080/03075070903452594
Wissinger, C. L. (2018). Is there a place for
undergraduate and graduate students in the systematic review process? Journal of the Medical Library Association,
106(2), 248-250. https://doi.org/10.5195/JMLA.2018.387
Appendix
Electronic database search strategies
Database(s): Ovid MEDLINE(R) and Epub Ahead
of Print, In-Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations and Daily 1946 to
September 11, 2020
|
# |
Searches |
|
1 |
meta-analysis as
topic/ |
|
2 |
"review
literature as topic"/ |
|
3 |
systematic reviews as
topic/ |
|
4 |
1 or 2 or 3 |
|
5 |
Teaching/mt or exp
Education, Continuing/mt or exp Education, Graduate/mt |
|
6 |
4 and 5 |
|
7 |
(("systematic
review*" or "meta-analys?s" or
"knowledge synthes?s" or "evidence synthes?s" or "research synthes?s"
or "metaanalys?s" or "rapid
review*" or "realist review*" or "realist synthes?s" or "integrative review*" or
"umbrella review*" or "review* of review*" or
"scoping review*") adj5 (teach or teaching or course or courses or
workshop* or instruct* or lecture* or tutorial* or curriculum or curricula or
curricular)).tw,kf. |
|
8 |
(("meta-synthes?s" or "metasynthes?s"
or "synthes?s method*" or "critical
interpretative synthes?s" or "meta-ethnograph*" or "meta-study" or
"meta-summar*" or "narrative synthes?s" or "qualitative synthes?s"
or "mixed method* synthes?s" or
"Multilevel synthes?s" or "Network
review*" or "Health technolog*
assessment*" or "network meta*" or "meta* review*")
adj5 (teach or teaching or course or courses or workshop* or instruct* or
lecture* or tutorial* or curriculum or curricula or curricular)).tw,kf. |
|
9 |
6 or 7 or 8 |
Database(s): Embase 1974 to 2020 September 11 (OVID)
|
# |
Searches |
|
1 |
"meta analysis (topic)"/ |
|
2 |
"systematic
review (topic)"/ |
|
3 |
1 or 2 |
|
4 |
*medical education/ |
|
5 |
*continuing education/ |
|
6 |
*nursing education/ |
|
7 |
*teaching/ |
|
8 |
4 or 5 or 6 or 7 |
|
9 |
8 and 3 |
|
10 |
(("systematic
review*" or "meta-analys?s" or
"knowledge synthes?s" or "evidence synthes?s" or "research synthes?s"
or "metaanalys?s" or "rapid
review*" or "realist review*" or "realist synthes?s" or "integrative review*" or
"umbrella review*" or "review* of review*" or
"scoping review*") adj5 (teach or teaching or course or courses or
workshop* or instruct* or lecture* or tutorial* or curriculum or curricula or
curricular)).tw,kw. |
|
11 |
(("meta-synthes?s" or "metasynthes?s"
or "synthes?s method*" or "critical
interpretative synthes?s" or "meta-ethnograph*" or "meta-study" or
"meta-summar*" or "narrative synthes?s" or "qualitative synthes?s"
or "mixed method* synthes?s" or
"Multilevel synthes?s" or "Network
review*" or "Health technolog*
assessment*" or "network meta*" or "meta* review*")
adj5 (teach or teaching or course or courses or workshop* or instruct* or
lecture* or tutorial* or curriculum or curricula or curricular)).tw,kw. |
|
12 |
9 or 10 or 11 |
|
13 |
limit 12 to (editorial
or letter or note or tombstone) |
|
14 |
12 not 13 |
Database(s): APA PsycInfo 1806 to
September Week 1 2020 (OVID)
|
# |
Searches |
|
1 |
meta analysis/ |
|
2 |
"literature review"/ |
|
3 |
1 or 2 |
|
4 |
*medical education/ |
|
5 |
*continuing education/ |
|
6 |
*nursing education/ |
|
7 |
*GRADUATE PSYCHOLOGY EDUCATION/
or *PSYCHOLOGY EDUCATION/ or *EDUCATION/ or *HEALTH EDUCATION/ or *graduate
education/ |
|
8 |
4 or 5 or 6 or 7 |
|
9 |
8 and 3 |
|
10 |
(("systematic
review*" or "meta-analys?s" or
"knowledge synthes?s" or "evidence synthes?s" or "research synthes?s"
or "metaanalys?s" or "rapid
review*" or "realist review*" or "realist synthes?s" or "integrative review*" or
"umbrella review*" or "review* of review*" or
"scoping review*") adj5 (teach or teaching or course or courses or
workshop* or instruct* or lecture* or tutorial* or curriculum or curricula or
curricular)).tw,hw. |
|
11 |
(("meta-synthes?s"
or "metasynthes?s" or "synthes?s method*" or "critical interpretative synthes?s" or "meta-ethnograph*"
or "meta-study" or "meta-summar*"
or "narrative synthes?s" or
"qualitative synthes?s" or "mixed
method* synthes?s" or "Multilevel synthes?s" or "Network review*" or
"Health technolog* assessment*" or
"network meta*" or "meta* review*") adj5 (teach or
teaching or course or courses or workshop* or instruct* or lecture* or
tutorial* or curriculum or curricula or curricular)).tw,hw. |
|
12 |
9 or 10 or 11 |
|
13 |
limit 12 to
("column/opinion" or "comment/reply" or editorial or
letter or obituary or poetry or review-book or review-media or
review-software & other) |
|
14 |
12 not 13 |
Academic Search Complete, Business Source Complete, CINAHL Plus with
Full-text, ERIC, Education Research Complete, Library & Information Science
Source, and SocINDEX (via EBSCO) – searched together.
|
# |
Query |
Last Run Via |
|
S1 |
TI ( (("systematic review*" or "meta-analys?s"
or "knowledge synthes?s" or
"evidence synthes?s" or "research synthes?s" or "metaanalys?s"
or "rapid review*" or "realist review*" or “realist synthes?s” or "integrative review*" or
"umbrella review*" or “review* of review*” or “scoping review*”) N5
(teach or teaching or course or courses or workshop* or instruct* or lecture*
or tutorial* or curriculum or curricula or curricular)) ) OR AB (
(("systematic review*" or "meta-analys?s"
or "knowledge synthes?s" or
"evidence synthes?s" or "research synthes?s" or "metaanalys?s"
or "rapid review*" or "realist review*" or “realist synthes?s” or "integrative review*" or
"umbrella review*" or “review* of review*” or “scoping review*”) N5
(teach or teaching or course or courses or workshop* or instruct* or lecture*
or tutorial* or curriculum or curricula or curricular)) ) |
Interface - EBSCOhost Database - Academic Search Complete; Business Source Complete; CINAHL Plus with
Full Text; Library & Information Science Source; SocINDEX
with Full Text; ERIC; Education Research Complete |
|
S2 |
TI ( ((“meta-synthes?s” or “metasynthes?s” or “synthes?s
method*” OR “critical interpretative synthes?s” OR
“meta-ethnograph*” OR “meta-study” OR “meta-summar*” OR “narrative synthes?s”
OR “qualitative synthes?s” OR “mixed method* synthes?s” OR “Multilevel synthes?s”
OR “Network review*” OR “Health technolog*
assessment*” OR “network meta*” or “meta* review*”) N5 (teach or teaching or
course or courses or workshop* or instruct* or lecture* or tutorial* or
curriculum or curricula or curricular)) ) OR AB ( ((“meta-synthes?s”
or “metasynthes?s” or “synthes?s
method*” OR “critical interpretative synthes?s” OR
“meta-ethnograph*” OR “meta-study” OR “meta-summar*” OR “narrative synthes?s”
OR “qualitative synthes?s” OR “mixed method* synthes?s” OR “Multilevel synthes?s”
OR “Network review*” OR “Health technolog*
assessment*” OR “network meta*” or “meta* review*”) N5 (teach or teaching or
course or courses or workshop* or instruct* or lecture* or tutorial* or
curriculum or curricula or curricular)) ) |
Interface - EBSCOhost Database - Academic Search Complete; Business Source Complete; CINAHL Plus with
Full Text; Library & Information Science Source; SocINDEX
with Full Text; ERIC; Education Research Complete |
|
S3 |
S1 OR S2 |
|
Web of Science Core Collection (which
includes: SCI-EXPANDED, SSCI, A&HCI, CPCI-S, CPCI-SSH, ESCI.)
|
# |
Search |
|
1 |
TOPIC: ((((("systematic review*" or "meta-analys?s" or "knowledge synthes?s" or "evidence synthes?s"
or "research synthes?s" or "metaanalys?s" or "rapid review*" or
"realist review*" or “realist synthes?s”
or "integrative review*" or "umbrella review*" or “review*
of review*” or “scoping review*”) NEAR/5 (teach or teaching or course or
courses or workshop* or instruct* or lecture* or tutorial* or curriculum or
curricula or curricular))))) |
|
2 |
TOPIC: (((((“meta-synthes?s”
or “metasynthes?s” or “synthes?s
method*” OR “critical interpretative synthes?s” OR
“meta-ethnograph*”
OR “meta-study” OR “meta-summar*” OR
“narrative synthes?s” OR “qualitative synthes?s” OR “mixed method* synthes?s” OR “Multilevel synthes?s” OR “Network review*” OR “Health technolog*
assessment*” OR “network meta*” or
“meta* review*”) NEAR/5 (teach or teaching or course or courses or workshop*
or instruct* or lecture* or tutorial* or curriculum or curricula or
curricular))))) |
|
3 |
1 OR 2 |
Library & Information Science Abstracts (via ProQuest)
|
# |
Search |
|
S1 |
ti(((((“meta-synthes?s” or “metasynthes?s”
or “synthes?s method*” OR “critical interpretative synthes?s” OR “meta-ethnograph*”
OR “meta-study” OR “meta-summar*” OR “narrative synthes?s” OR “qualitative synthes?s”
OR “mixed method* synthes?s” OR “Multilevel synthes?s” OR “Network review*” OR “Health technolog* assessment*” OR “network meta*” or “meta*
review*”) NEAR/5 (teach or teaching or course or courses or workshop* or
instruct* or lecture* or tutorial* or curriculum or curricula or
curricular))))) OR ab(((((“meta-synthes?s” or “metasynthes?s” or “synthes?s
method*” OR “critical interpretative synthes?s” OR
“meta-ethnograph*” OR “meta-study” OR “meta-summar*” OR “narrative synthes?s”
OR “qualitative synthes?s” OR “mixed method* synthes?s” OR “Multilevel synthes?s”
OR “Network review*” OR “Health technolog*
assessment*” OR “network meta*” or “meta* review*”) NEAR/5 (teach or teaching
or course or courses or workshop* or instruct* or lecture* or tutorial* or
curriculum or curricula or curricular))))) |
|
S2 |
ti((((("systematic
review*" or "meta-analys?s" or
"knowledge synthes?s" or "evidence synthes?s" or "research synthes?s"
or "metaanalys?s" or "rapid
review*" or "realist review*" or “realist synthes?s”
or "integrative review*" or "umbrella review*" or
“review* of review*” or “scoping review*”) NEAR/5 (teach or teaching or
course or courses or workshop* or instruct* or lecture* or tutorial* or
curriculum or curricula or curricular))) )) OR ab((((("systematic
review*" or "meta-analys?s" or
"knowledge synthes?s" or "evidence synthes?s" or "research synthes?s"
or "metaanalys?s" or "rapid
review*" or "realist review*" or “realist synthes?s”
or "integrative review*" or "umbrella review*" or
“review* of review*” or “scoping review*”) NEAR/5 (teach or teaching or
course or courses or workshop* or instruct* or lecture* or tutorial* or
curriculum or curricula or curricular))) )) |
|
S3 |
S1 OR S2 |