Reflections on Rasāyana, Bcud Len and Related Practices in Nyingma (Rnying Ma) Tantric Ritual
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.18732/hssa.v5i2.17Abstract
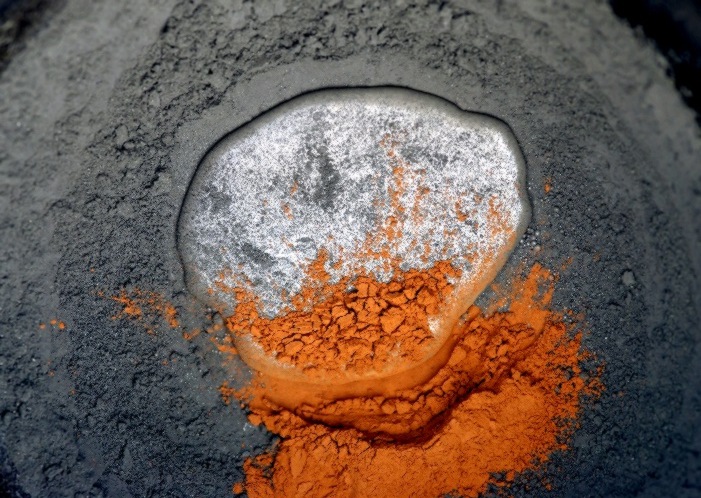
The Tibetan term, bcud len, "imbibing the essence juice", is considered an equivalent for the Sanskrit term, rasāyana. But in Tibetan Buddhist ritual manuals, both terms occur, apparently with slightly different connotations. Practices classified as bcud len are frequently relatively short, and seem primarily designed for the use of individual yogis, usually as a subsidiary practice to complement their main tantric meditation. The production of bcud len pills which are said to sustain, rejuvenate and extend the life of the body, or even to bring immortality, is often an integral part of the practice. The term, rasāyana, is used in Tibetan transliteration (ra sā ya na), not as a title or classification for a specific ritual practice or recipe for pills, but rather to refer to the processes of alchemical transformation of substances within complex ritual "medicinal accomplishment" (sman sgrub) performances which are generally communal. In this case too, pills are produced, of the broader "sacred elixir dharma medicine" (dam rdzas bdud rtsi chos sman) type. This paper will consider a range of the practices, and of substances used in the sacred medicinal compounds.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2017 Catherine Cantwell

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike license that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).